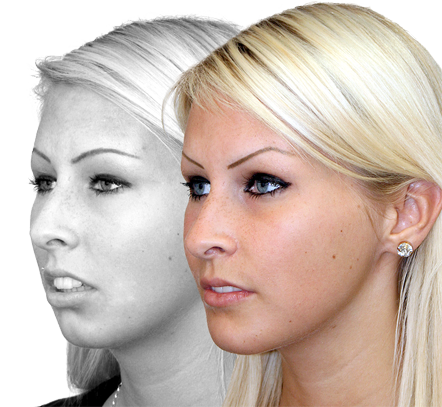
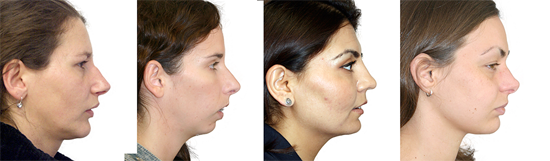
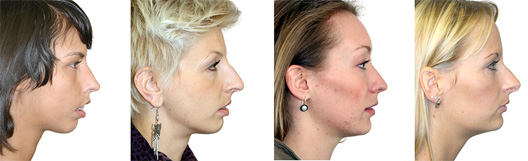
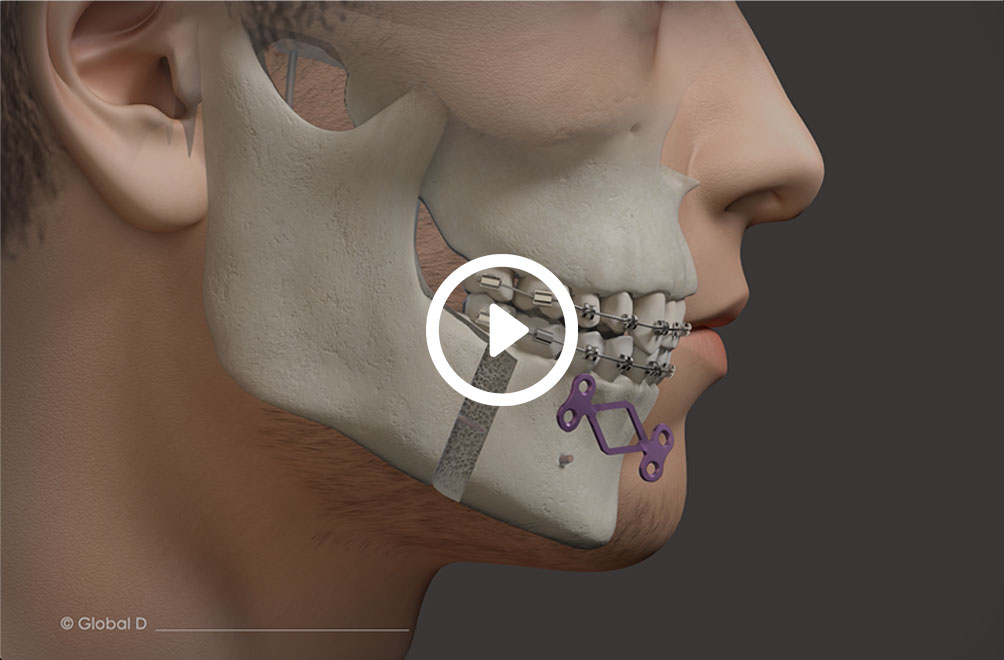
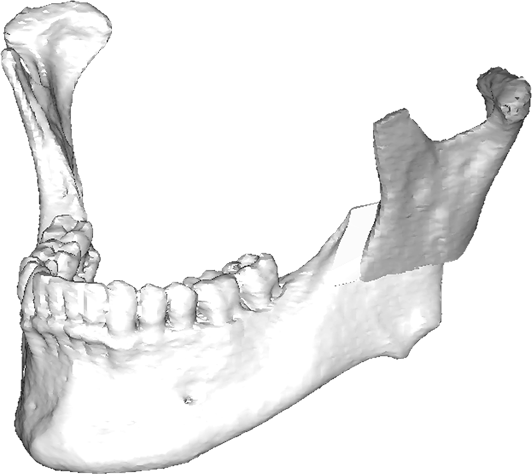
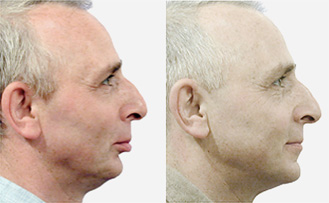
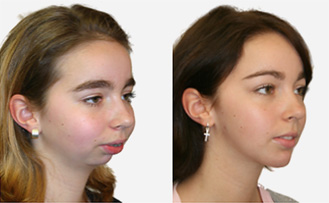
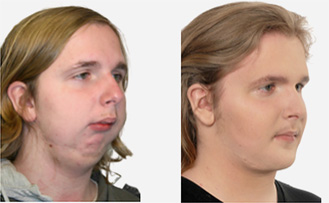
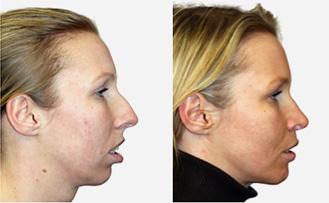
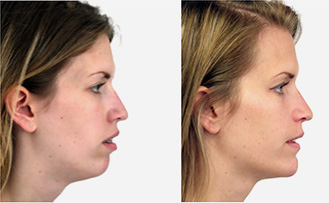
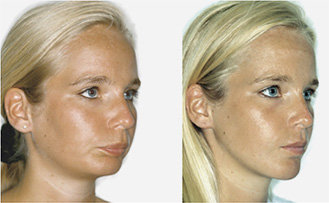
maxillary / mandibular recession /
facial asymmetries
Repositioning the upper or lower jaw to create an optimal overbite and
profile normalization. Combination of upper and lower jaw surgery (maxillomandibular
realignment)